Giải phương trình
a) x4 - 3x3 + 4x2 - 3x - 1 = 0
b) 3x4 - 15x3 + 16x2 - 13x + 2 = 0
c) x5 + 2x4 + 3x3 + 2x + 1 = 0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a, \(x^4-4x^3-6x^2-4x+1=0\)(*)
<=> \(x^4+4x^2+1-4x^3-4x+2x^2-12x^2=0\)
<=> \(\left(x^2-2x+1\right)^2=12x^2\)
<=>\(\left(x-1\right)^4=12x^2\) <=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-1\right)^2=\sqrt{12}x\\\left(x-1\right)^2=-\sqrt{12}x\end{matrix}\right.\)<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-2x+1-\sqrt{12}x=0\left(1\right)\\x^2-2x+1+\sqrt{12}x=0\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Giải (1) có: \(x^2-2x+1-\sqrt{12}x=0\)
<=> \(x^2-2x\left(1+\sqrt{3}\right)+\left(1+\sqrt{3}\right)^2-\left(1+\sqrt{3}\right)^2+1=0\)
<=> \(\left(x-1-\sqrt{3}\right)^2-3-2\sqrt{3}=0\)
<=> \(\left(x-1-\sqrt{3}\right)^2=3+2\sqrt{3}\) <=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1-\sqrt{3}=\sqrt{3+2\sqrt{3}}\\x-1-\sqrt{3}=-\sqrt{3+2\sqrt{3}}\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{3+2\sqrt{3}}+\sqrt{3}+1\left(ktm\right)\\x=-\sqrt{3+2\sqrt{3}}+\sqrt{3}+1\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
=> \(x=-\sqrt{3+2\sqrt{3}}+\sqrt{3}+1\)
Giải (2) có: \(x^2-2x+1+\sqrt{12}x=0\)
<=> \(x^2-2x\left(1-\sqrt{3}\right)+\left(1-\sqrt{3}\right)^2-\left(1-\sqrt{3}\right)^2+1=0\)
<=> \(\left(x+\sqrt{3}-1\right)^2=3-2\sqrt{3}\) .Có VP<0 => PT (2) vô nghiệm
Vậy pt (*) có nghiệm x=\(-\sqrt{3+2\sqrt{3}}+\sqrt{3}+1\)

a) x 4 – 5 x 2 + 4 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 = t, điều kiện t ≥ 0.
Khi đó (1) trở thành : t 2 – 5 t + 4 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2) : Có a = 1 ; b = -5 ; c = 4 ⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm t 1 = 1 ; t 2 = c / a = 4
Cả hai giá trị đều thỏa mãn điều kiện.
+ Với t = 1 ⇒ x 2 = 1 ⇒ x = 1 hoặc x = -1;
+ Với t = 4 ⇒ x 2 = 4 ⇒ x = 2 hoặc x = -2.
Vậy phương trình (1) có tập nghiệm S = {-2 ; -1 ; 1 ; 2}.
b) 2 x 4 – 3 x 2 – 2 = 0 ; ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 = t , điều kiện t ≥ 0.
Khi đó (1) trở thành : 2 t 2 – 3 t – 2 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2) : Có a = 2 ; b = -3 ; c = -2
⇒ Δ = ( - 3 ) 2 - 4 . 2 . ( - 2 ) = 25 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm
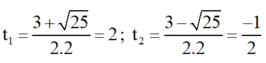
Chỉ có giá trị t 1 = 2 thỏa mãn điều kiện.
+ Với t = 2 ⇒ x 2 = 2 ⇒ x = √2 hoặc x = -√2;
Vậy phương trình (1) có tập nghiệm S = {-√2 ; √2}.
c) 3 x 4 + 10 x 2 + 3 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 = t , điều kiện t ≥ 0.
Khi đó (1) trở thành : 3 t 2 + 10 t + 3 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2) : Có a = 3; b' = 5; c = 3
⇒ Δ ’ = 5 2 – 3 . 3 = 16 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt
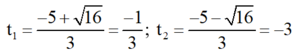
Cả hai giá trị đều không thỏa mãn điều kiện.
Vậy phương trình (1) vô nghiệm.

1.
a/ \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+3x+2\right)+\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-3x+2\right)-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+2\right)+3x\left(x+1\right)-3x\left(x-1\right)+\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+2\right)-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x\left(x^2+2\right)+6x^2-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+3x^2+2x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+4x+6\right)=0\Rightarrow x=1\)
b/ Nhận thấy \(x=0\) ko phải nghiệm, chia 2 vế cho \(x^2\)
\(x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}+3\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)+4=0\)
Đặt \(x+\frac{1}{x}=t\Rightarrow x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}=t^2-2\)
\(t^2-2+3t+4=0\Rightarrow t^2+3t+2=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=-1\\t=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+\frac{1}{x}=-1\\x+\frac{1}{x}=-2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+x+1=0\left(vn\right)\\x^2+2x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow x=-1\)
1c/
\(\Leftrightarrow x^5+x^4-2x^4-2x^3+5x^3+5x^2-2x^2-2x+x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4\left(x+1\right)-2x^3\left(x+1\right)+5x^2\left(x+1\right)-2x\left(x+1\right)+x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^4-2x^3+5x^2-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x^4-2x^3+5x^2-2x+1=0\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow x^4-2x^3+x^2+x^2-2x+1+3x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-x\right)^2+\left(x-1\right)^2+3x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-x=0\\x-1=0\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\) không tồn tại x thỏa mãn
Vậy pt có nghiệm duy nhất \(x=-1\)


Ta có : x4+3x3+4x2+3x+1=0
⇔ ( x4 + x3 ) + ( 2x3 + 2x2 ) + ( 2x2 + 2x ) + ( x + 1 ) = 0
⇔ x3 ( x + 1 ) + 2x2 ( x + 1 ) + 2x ( x+1 ) + ( x + 1 ) =0
⇔ ( x + 1 ) ( x3 + 2x2 + 2x + 1 ) = 0
⇔ ( x + 1 ) [ ( x3 + 1 ) + ( 2x2 + 2x ) ] = 0
⇔ ( x + 1 ) [ (x + 1 ) ( x2 - x +1 ) + 2x ( x + 1 ) ] =0
⇔ ( x +1 ) ( x + 1 ) ( x2 + x +1 ) =0
⇒ \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\x^{2^{ }}+x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}=0\left(VoLy\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy x = -1
x4+3x3+4x2+3x+1=0
⇔(x4+2x3+x2)+(x3+2x2+1)+(x2+2x+1)=0
⇔x2(x2+2x+1)+x(x2+2x+1)+(x2+2x+1)=0
⇔x2(x+1)2+x(x+1)2+(x+1)2=0
⇔(x+1)2(x2+x+1)=0
Vì x2+x+1=x2+x+\(\dfrac{1}{4}\)+\(\dfrac{3}{4}\)=(x+\(\dfrac{1}{2}\))2+\(\dfrac{3}{4}\)>0 nên phương trình đã cho tương đương:
(x+1)2=0 ⇔(x+1)(x+1)=0 ⇔x=-1.

a: \(\dfrac{2x^4-3x^3+4x^2+1}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{2x^4-2x^2-3x^3+3x+6x^2-6-3x+7}{x^2-1}\)
\(=2x^2-3x+6+\dfrac{-3x+7}{x^2-1}\)
Để dư bằng 0 thì -3x+7=0
=>x=7/3
b: \(\dfrac{x^5+2x^4+3x^2+x-3}{x^2+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^5+x^3+2x^4+2x^2-x^3-x+x^2+1+2x-4}{x^2+1}\)
\(=x^3+2x^2-x+1+\dfrac{2x-4}{x^2+1}\)
Để đư bằng 0 thì 2x-4=0
=>x=2

a: f(x)=3x^4+2x^3+6x^2-x+2
g(x)=-3x^4-2x^3-5x^2+x-6
f(x)+g(x)
=3x^4+2x^3+6x^2-x+2-3x^4-2x^3-5x^2+x-6
=x^2-4
f(x)-g(x)
=3x^4+2x^3+6x^2-x+2+3x^4+2x^3+5x^2-x+6
=6x^4+4x^3+11x^2-2x+8
\(x^4-3x^3+4x^2-3x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+x^3+2x^3+2x^2+2x^2+2x+x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3\left(x+1\right)+2x^2\left(x+1\right)+2x\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3+2x^2+2x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^3+2x^2+2x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow(x^3+x^2+x^2+x+x+1)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow[x^2\left(x+1\right)+x\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+1\right)]\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}(x+1)^2=0\\x^2+x+1=0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\\varnothing\end{cases}}\Rightarrow x=-1\)