Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Cho hàm số y=f(x)y=f(x) có đạo hàm và liên tục trên [0;π2][0;π2]thoả mãn f(x)=f′(x)−2cosxf(x)=f′(x)−2cosx. Biết f(π2)=1f(π2)=1, tính giá trị f(π3)f(π3)
A. √3+1/2 B. √3−1/2 C. 1−√3/2 D. 0

a) Điều kiện x>0. Thực hiện chia tử cho mẫu ta được:
f(x) = =
=
∫f(x)dx = ∫()dx =
+C
b) Ta có f(x) = =
-e-x
; do đó nguyên hàm của f(x) là:
F(x)= =
=
+ C
c) Ta có f(x) =
hoặc f(x) =
Do đó nguyên hàm của f(x) là F(x)= -2cot2x + C
d) Áp dụng công thức biến tích thành tổng:
f(x) =sin5xcos3x = (sin8x +sin2x).
Vậy nguyên hàm của hàm số f(x) là F(x) = -(
cos8x + cos2x) +C
e) ta có
vậy nguyên hàm của hàm số f(x) là F(x) = tanx - x + C
g) Ta có ∫e3-2xdx= -∫e3-2xd(3-2x)= -
e3-2x +C
h) Ta có :
= =

Làm xuôi thì đơn giản, tính \(F'\left(x\right)\) là xong (chịu khó biến đổi)
Làm ngược thì nhìn biểu thức hơi thiếu thân thiện
\(\int\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}\left(x^2-1\right)}{x^4+1}dx=\int\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}\left(x^2-1\right)}{\left(x^2-x\sqrt{2}+1\right)\left(x^2+x\sqrt{2}+1\right)}dx\)
Phân tách hệ số bất định:
\(\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}\left(x^2-1\right)}{\left(x^2-x\sqrt{2}+1\right)\left(x^2+x\sqrt{2}+1\right)}=\dfrac{a\left(2x-\sqrt{2}\right)}{x^2-x\sqrt{2}+1}+\dfrac{b\left(2x+\sqrt{2}\right)}{x^2+x\sqrt{2}+1}\)
Quan tâm tử số: \(a\left(2x-\sqrt{2}\right)\left(x^2+x\sqrt{2}+1\right)+b\left(2x+\sqrt{2}\right)\left(x^2-x\sqrt{2}+1\right)\)
\(=2\left(a+b\right)x^3+\sqrt{2}\left(a-b\right)x^2+\sqrt{2}\left(b-a\right)\)
Đồng nhất 2 tử số: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=0\\a-b=2\\\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=1\\b=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do đó:
\(\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}\left(x^2-1\right)}{x^4+1}=\dfrac{2x-\sqrt{2}}{x^2-x\sqrt{2}+1}-\dfrac{2x+\sqrt{2}}{x^2+x\sqrt{2}+1}\)
Cái tìm hệ số bất định ấy ạ, tại sao lại tách về 2x- căn 2 vậy anh?

a: \(y=\left(2x^2-x+1\right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}\)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{1}{3}\left(2x^2-x+1\right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}-1}\cdot\left(2x^2-x+1\right)'\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{3}\cdot\left(4x-1\right)\left(2x^2-x+1\right)^{-\dfrac{2}{3}}\)
b: \(y=\left(3x+1\right)^{\Omega}\)
=>\(y'=\Omega\cdot\left(3x+1\right)'\cdot\left(3x+1\right)^{\Omega-1}\)
=>\(y'=3\Omega\left(3x+1\right)^{\Omega-1}\)
c: \(y=\sqrt[3]{\dfrac{1}{x-1}}\)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{\left(\dfrac{1}{x-1}\right)'}{3\cdot\sqrt[3]{\left(\dfrac{1}{x-1}\right)^2}}\)
\(=\dfrac{\dfrac{1'\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)'\cdot1}{\left(x-1\right)^2}}{\dfrac{3}{\sqrt[3]{\left(x-1\right)^2}}}\)
\(=\dfrac{-x}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt[3]{\left(x-1\right)^2}}{3}\)
\(=\dfrac{-x}{\sqrt[3]{\left(x-1\right)^4}\cdot3}\)
d: \(y=log_3\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y'=\dfrac{\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}\right)'}{\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}\cdot ln3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y'=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)'\left(x-1\right)-\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)'}{\left(x-1\right)^2}:\dfrac{ln3\left(x+1\right)}{x-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y'=\dfrac{x-1-x-1}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\cdot\dfrac{x-1}{ln3\cdot\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y'=\dfrac{-2}{\left(x-1\right)\cdot\left(x+1\right)\cdot ln3}\)
e: \(y=3^{x^2}\)
=>\(y'=\left(x^2\right)'\cdot ln3\cdot3^{x^2}=2x\cdot ln3\cdot3^{x^2}\)
f: \(y=\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^{x^2-1}\)
=>\(y'=\left(x^2-1\right)'\cdot ln\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^{x^2-1}=2x\cdot ln\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^{x^2-1}\)
h: \(y=\left(x+1\right)\cdot e^{cosx}\)
=>\(y'=\left(x+1\right)'\cdot e^{cosx}+\left(x+1\right)\cdot\left(e^{cosx}\right)'\)
=>\(y'=e^{cosx}+\left(x+1\right)\cdot\left(cosx\right)'\cdot e^u\)
\(=e^{cosx}+\left(x+1\right)\cdot\left(-sinx\right)\cdot e^u\)
a) \(y=\left(2x^2-x+1\right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}}\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=\dfrac{1}{3}.\left(2x^2-x+1\right)^{\dfrac{1}{3}-1}.\left(4x-1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=\dfrac{1}{3}.\left(2x^2-x+1\right)^{-\dfrac{2}{3}}.\left(4x-1\right)\)
b) \(y=\left(3x+1\right)^{\pi}\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=\pi.\left(3x+1\right)^{\pi-1}.3=3\pi.\left(3x+1\right)^{\pi-1}\)
c) \(y=\sqrt[3]{\dfrac{1}{x-1}}\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^{-1-1}}{3\sqrt[3]{\left(\dfrac{1}{x-1}\right)^{3-1}}}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^{-2}}{3\sqrt[3]{\left(\dfrac{1}{x-1}\right)^2}}=\dfrac{1}{3.\sqrt[]{x-1}.\sqrt[3]{\left(\dfrac{1}{x-1}\right)^2}}\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=\dfrac{1}{3\left(x-1\right)^{\dfrac{1}{2}}.\left(x-1\right)^{\dfrac{2}{3}}}=\dfrac{1}{3\left(x-1\right)^{\dfrac{7}{6}}}=\dfrac{1}{3\sqrt[6]{\left(x-1\right)^7}}\)
d) \(y=\log_3\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=\dfrac{\dfrac{1-\left(-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}}{\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}.\ln3}=\dfrac{2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right).\ln3}\)
e) \(y=3^{x^2}\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=3^{x^2}.ln3.2x=2x.3^{x^2}.ln3\)
f) \(y=\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^{x^2-1}\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^{x^2-1}.ln\dfrac{1}{2}.2x=2x.\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^{x^2-1}.ln\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Các bài còn lại bạn tự làm nhé!

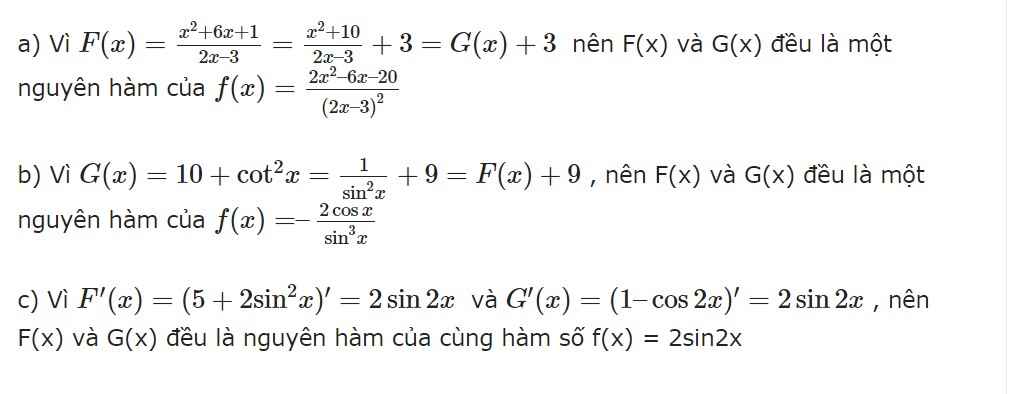

Để kiểm tra một hàm F(x) có phải là một nguyên hàm của f(x) không thì ta chỉ cần kiểm tra F'(x) có bằng f(x) không?
a) \(F\left(x\right)\) là hằng số nên \(F'\left(x\right)=0\ne f\left(x\right)\)
b) \(G'\left(x\right)=2.\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{1}{\cos^2x}=1+\tan^2x\)
c) \(H'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{\cos x}{1+\sin x}\)
d) \(K'\left(x\right)=-2.\dfrac{-\left(\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{1}{\cos^2\dfrac{x}{2}}\right)}{\left(1+\tan\dfrac{x}{2}\right)^2}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{\cos^2\dfrac{x}{2}}}{\left(\dfrac{\cos\dfrac{x}{2}+\sin\dfrac{x}{2}}{\cos\dfrac{x}{2}}\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{\left(\cos\dfrac{x}{2}+\sin\dfrac{x}{2}\right)^2}=\dfrac{1}{1+2\cos\dfrac{x}{2}\sin\dfrac{x}{2}}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{1+\sin x}\)
Vậy hàm số K(x) là một nguyên hàm của f(x).