a) Tìm các giá trị nguyên của \(x\) để biểu thức M=\(\dfrac{8x+1}{4x-1}\)nhận giá trị nguyên
b) Tìm giá trị nguyên của biến \(x\) để biểu thức \(A=\dfrac{5}{4-x}\)có giá trị lớn nhất
c) Tìm giá trị nguyên của biến \(x\) để biểu thức \(B=\dfrac{8-x}{x-3}\)có giá trị nhỏ nhất
(Hơi khó mọi người giúp mình với ạ)




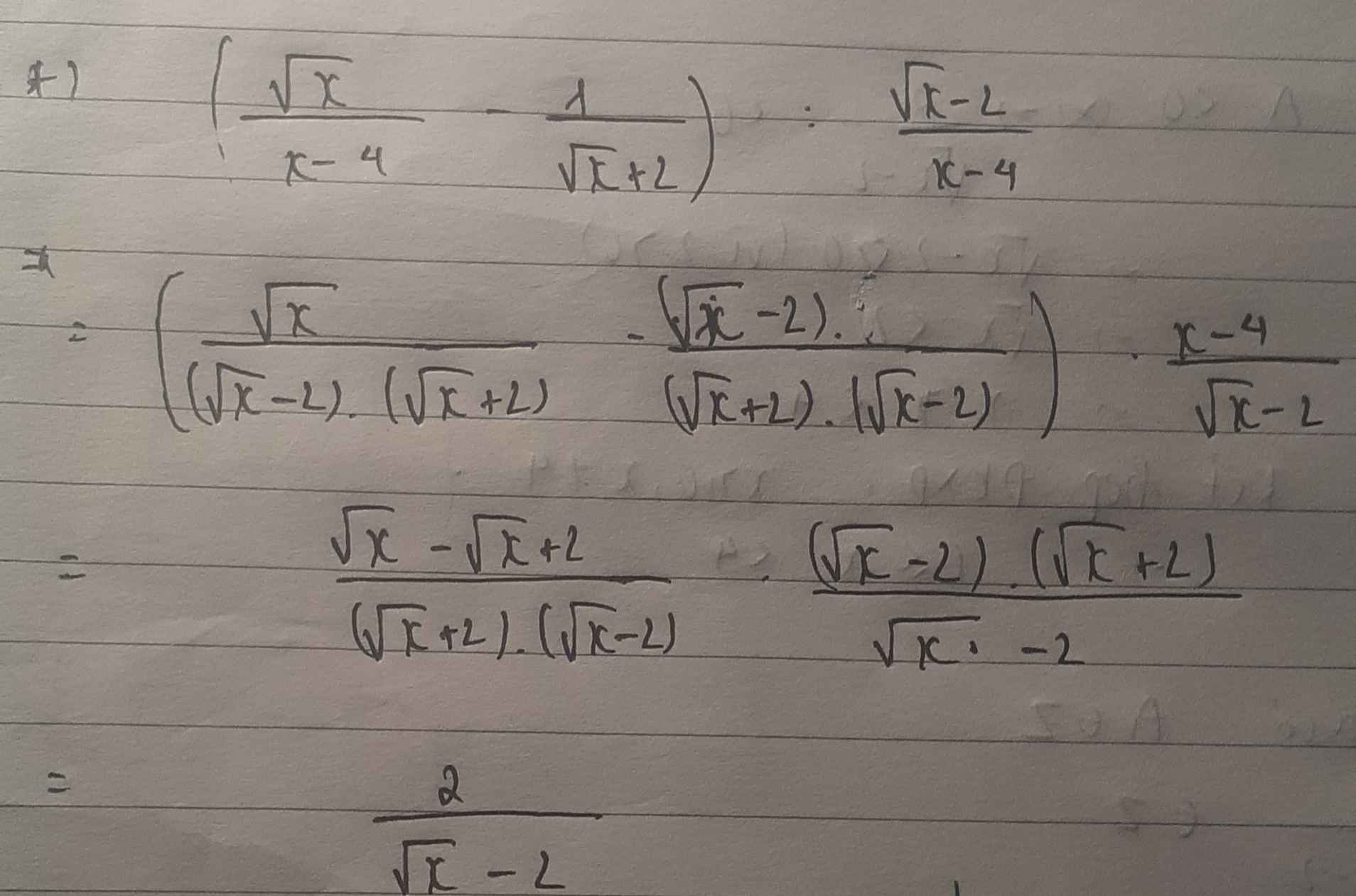
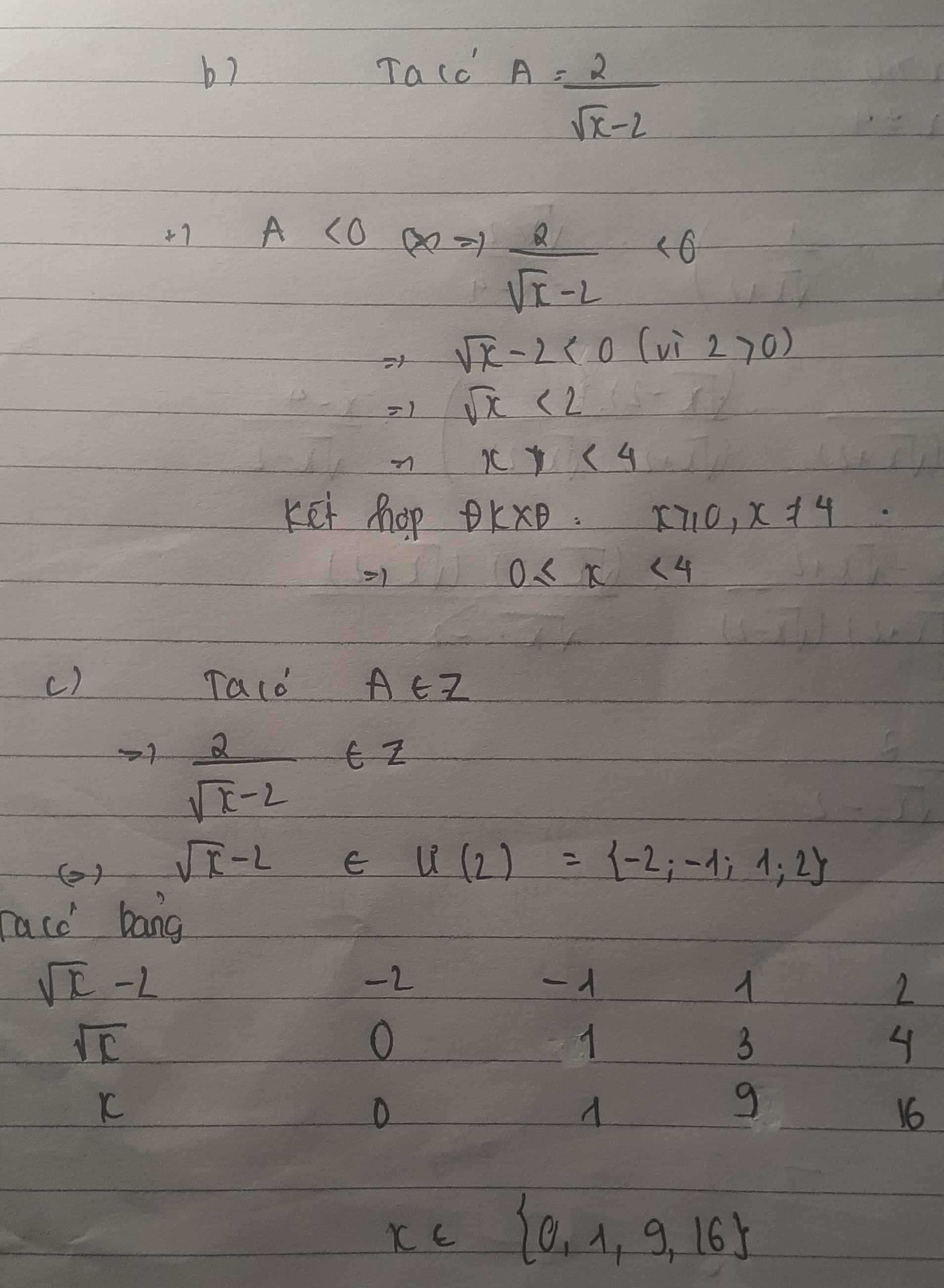

a) Ta có: \(M=\dfrac{8x+1}{4x-5}=\dfrac{8x-10+11}{4x-5}=\dfrac{2\left(x-5\right)+11}{4x-5}=2+\dfrac{11}{4x-5}\)
Để M nhận giá trị nguyên thì \(2+\dfrac{11}{4x-5}\) nhận giá trị nguyên
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{11}{4x-5}\) nhận giá trị nguyên
\(\Rightarrow11⋮4x-5\)
Vì \(x\in Z\) nên \(4x-5\in Z\)
\(\Rightarrow4x-5\inƯ\left(11\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm11\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{1;\pm1,5;4\right\}\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{1;4\right\}\) thỏa mãn \(x\in Z\).
b) Ta có: \(A=\dfrac{5}{4-x}\). ĐK: \(x\ne4\)
Nếu 4 - x < 0 thì x > 4 \(\Rightarrow A>0\)
4 - x > 0 thì x < 4 \(\Rightarrow A< 0\)
Để A đạt GTLN thì 4 - x là số nguyên dương nhỏ nhất
\(\Rightarrow4-x=1\Rightarrow x=3\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{5}{4-3}=5\)
Vậy MaxA = 5 tại x = 3
c) \(B=\dfrac{8-x}{x-3}\). ĐK: \(x\ne3\).
Ta có: \(B=\dfrac{8-x}{x-3}=\dfrac{-\left(x-8\right)}{x-3}=\dfrac{-\left(x-3\right)+5}{x-3}=\dfrac{5}{x-3}-1\)
Để B đạt giá trị nhỏ nhất thì \(\dfrac{5}{x-3}-1\) nhỏ nhất
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{5}{x-3}\) nhỏ nhất
Nếu x - 3 > 0 thì x > 3 \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{5}{x-3}>0\)
x - 3 < 0 thì x < 3 \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{5}{x-3}< 0\)
Để \(\dfrac{5}{x-3}\) nhỏ nhất thì x - 3 là số nguyên âm lớn nhất
\(\Rightarrow x-3=-1\Rightarrow x=2\)
\(\Rightarrow B=\dfrac{8-2}{2-3}=-6\)
Vậy MaxB = -6 tại x = 2.
Mình làm sai câu a...
Ta có: \(M=\dfrac{8x+1}{4x-1}=\dfrac{8x-2+3}{4x-1}=\dfrac{2\left(4x-1\right)+3}{4x-1}=2+\dfrac{3}{4x-1}\)
Để M nhận giá trị nguyên thì \(2+\dfrac{3}{4x-1}\) nhận giá trị nguyên
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{3}{4x-1}\) nhận giá trị nguyên
Vì \(4x-1\in Z\) nên \(4x-1\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm3\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{\pm0,5;0;1\right\}\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{0;1\right\}\) thỏa mãn \(x\in Z\).